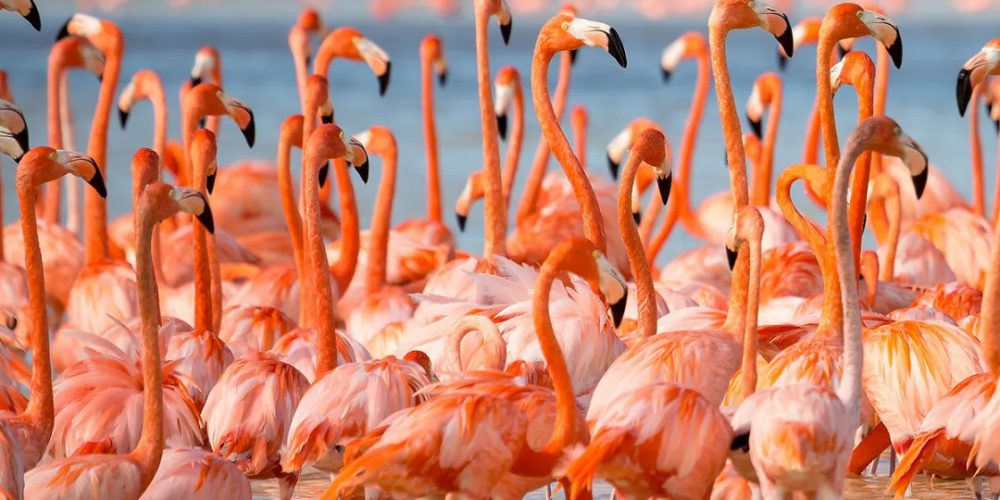
Grazing bison are excellent engineers in creating a healthy, vibrant ecosystem of prairies
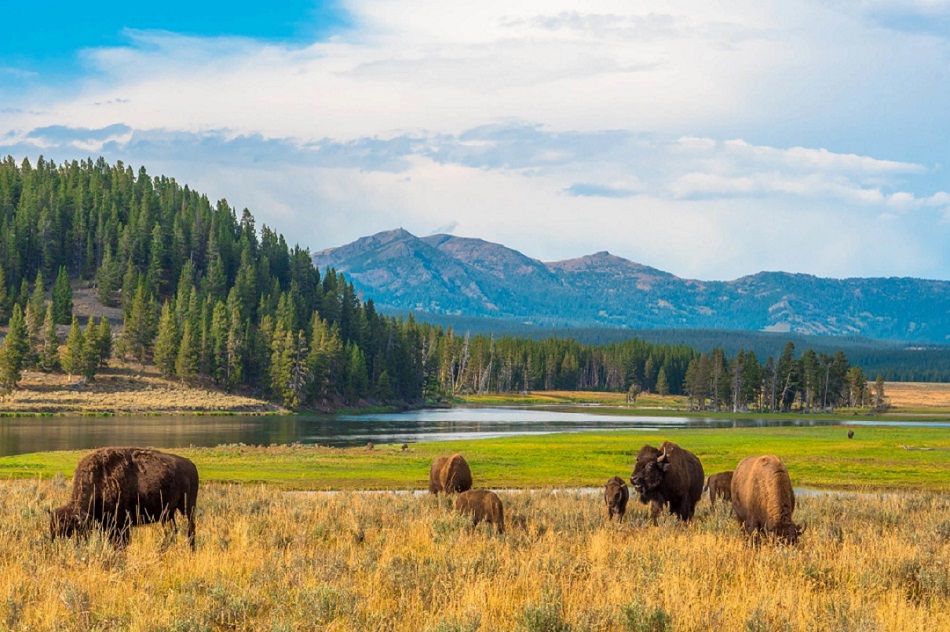

The rare wildlife of Montana’s shortgrass prairies, once thriving, is now in ecological decline.
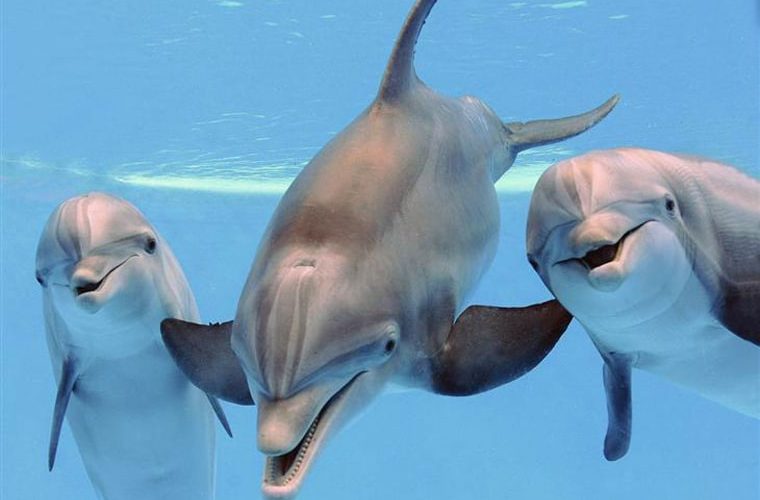
American bison, excellent engineers of the prairie ecosystem, who have been taking care of the ecological well-being of these places for many millennia, were almost completely exterminated as a result of hunting by European settlers.
Environmentalists and indigenous peoples of the Americas are now pinning their hopes on plains bison that they will make their important contribution to repairing the damage caused to the prairies by decades of poor management.
The places here are harsh. It takes mettle to live on Montana’s shortgrass prairie. It’s dry, windy and a long way from anywhere. In summer, temperatures can top 100F (38C). In winter, the mercury plunges to -50F (-45C). In some spots, it is more than an hour’s drive on gravel roads to buy a loaf of bread.
The indigenous Blackfeet, Nakoda and Gros Ventre peoples successfully adapted to the harsh environment over many centuries. More recently, a handful of hardy white settlers managed it too. The shortgrass prairie makes up 71 million hectares (27,413 sq miles) of remote land straddling the US/Canadian border to the east of the Rocky Mountains. For the last 150 years, wildlife have surrendered the prime habitat to cows. Crested wheatgrass, a non-native plant seeded by European settlers for their cattle, paints swathes of land yellow in summer.
Today, though, parts of the landscape are being shaped by a different resident. This one sports a pair of black horns and a thick cape of curly brown hair.

The North American plains bison has a long history here, albeit one that suffered a brutal interruption. For a century and a half, their distinctive humped shoulders and bearded faces were missing from America’s grasslands.
Tribes and conservation organisations have recently started bringing the bison back. And scientists studying the returns are discovering that getting the 2,000lb (900kg) grazer back in its native ecosystem could be key to the future of the prairie. Many wonder what a giant, fur-covered herbivore is doing to help save the prairie.
The bison’s biggest service is to assist the prairie in holding onto its water. Bison on the shortgrass prairie send a strong message about the importance of native grazers for landscape resilience. They may offer the prairie a lifeline as climate change tightens its grip.
Hila Shamon, a research ecologist with the Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute in Washington DC, has spent five years tracking the ecology of the remote grasslands.

She partners with American Prairie, a conservation organisation with parcels of land on either side of the million acre Charles M Russell National Wildlife Refuge, to study how bison are changing the ecosystem. Shamon spends her field season crawling across American Prairie property measuring everything from vegetation density and species diversity to the habits of grassland birds and prairie dogs.
Shamon recently co-authored a study on prairie streams which suggests bison do something remarkable in this hostile environment. “There is no doubt, year-round grazing of bison is good for the landscape,” she says. Bison, it turns out, have an ingrained capacity to boost biodiversity.

Plains bison co-evolved with the short-grass prairie. In the 12,000 years since the end of the Pleistocene, they have proven themselves to be potent ecosystem engineers.
An adult bison eats about 25lb (11kg) of grass a day. The grasses adapted to their foraging. Vegetation across the plains uses the nutrients in their dung. Birds pluck their fur from bushes to insulate their nests.
Bison also shape the land literally. They roll in the dust and create indentations known as “wallows” that hold water after rainstorms. After the bison move on, insects flourish in these pools and become a feast for birds and small mammals. Pronghorn antelope survive by following their tracks through deep winter snows.
Today, however, bison are getting a second chance
Plains bison spent thousands of years engineering a distinctive grassland ecology from Northern Canada through Montana to Mexico. But more than a century ago, this influence abruptly stopped. A few decades of slaughter led bison numbers to plummet from 60 million to barely 800 living wild in the US and Canada by 1889. Market forces and government policy replaced bison and native people with ranches, white settlement and cattle. For a hundred years, cattle claimed the prairie as their own. But while they were easier to turn into steaks, they were not as finely tuned for prairie life.
Today, however, bison are getting a second chance. Tribal reservations are at the forefront of their recovery.

They take excess bison from Yellowstone National Park and restoring them to treaty lands. American Prairie is also playing a part, buying ranches and returning bison to places where cattle were once king. About 30,000 bison now exist in conservation herds in various parks and protected areas across the country. More than 10 times that number exist on bison farms.
Scientists like Shamon are watching it all closely to see how the return of bison affects the land.
“Cows don’t move as much,” Shamon says. When the weather gets hot, they gravitate to the creek bottoms for shade and the cooling water. When it’s cold, cows hunker down behind creekside shrubs to shelter from the wind. This preference for spending time in the riparian zone starts a vicious cycle.

By browsing the trees and shrubs they reduce the amount of available shade, Shamon says. Their chewing means less leaf litter to cover the ground and, when the shrubs die, less roots to stabilise the stream banks. Over time, the soil around the creeks dries out, the boxelder, cottonwoods, wild rose and snowberry disappear, and the streambanks get taken over by non-native grasses. What was once a cooling refuge for wildlife becomes almost as forbidding as the uplands.
Bison, by contrast, are quite happy to tough it out on the prairie. It’s what evolution finetuned them to do. They visit streams and ponds periodically to drink, but bison were built to keep moving. Unless the temperatures approach the hundreds, they generally don’t bother spending time near creeks. They don’t need as much shade. They prefer the grasses on the sunbaked uplands to woody shrubs in the river bottoms. As a result, they do less damage to creeks than cows.
Although rivers and streams cover less than 2% of the prairie, they are crucial refuges for its wildlife. Shamon’s study shows increases in vegetation and bird diversity on creeks where bison have replaced cattle.

She also found more deer and elk. Other studies show that year-round, low-density grazing by bison is associated with more variety in woody vegetation heights and more native plant diversity in riparian areas than seasonal grazing by cattle. Well-vegetated creeks are the prairie’s lifeblood. They keep the soil moist, the vegetation green, and they provide dispersal corridors for large mammals like mountain lions and black bears. One day, they may provide safe passage for recovering grizzly bears.
The abundance of new growth made possible by the bison gave beavers the building material they needed
The stretch of Beaver Creek was changed by American Prairie, the non-profit wildlife restoration organization, from cattle grazing to bison in 2017. “When we bought this property, Beaver Creek looked like a single channel,” says Danny Kinka, American Prairie’s Senior Manager.

The area around Beaver Creek was the second piece of American Prairie property to hold bison after Sun Prairie 20 miles to the south-east. One hundred and fifty bison had 12,000 acres (4,856 hectares) on which to graze. Replacing cattle with bison has greened up a floodplain nearly 180m (594ft) wide.
Kinka explains how the bison had set the stage for beavers – nature’s other great restorationist – to help bring the landscape back to health. The abundance of new growth made possible by the bison gave beavers the building material they needed. Beavers make their dams from mud and cattails. Over the years to come, the flooding created by the dams will cause cottonwood seeds buried in the streambanks to sprout, leading to the regrowth of trees, says Kinka. As more shrubsand trees return, more beavers will move in and build more dams, he adds. The virtuous cycle will continue.

Kinka warns that if a creek channel has degraded too far it might need assistance getting to the point where it can spill water onto the floodplain again. The Montana Conservation Corps is an organisation putting Montana youth to work rehabilitating public and private lands. They pound barriers made of wooden posts, brush and mud in the creek to partially block water during spring runoff. The structures, known as Beaver Dam Analogues (or BDAs), slow the water, trapping sediment and raising the creek bed. It’s a technique known as low-tech process-based restoration.
“We don’t do it with backhoes [diggers],” Kinka says. “We do it with people in waders.” Sometimes a few BDAs can raise the water table enough to get a real beaver to move in and take over. Here on Beaver Creek, this hard work wasn’t necessary. What excites Kinka about the recovery here is its simplicity. “We didn’t go down there, we didn’t reintroduce beavers, we didn’t build BDAs. We didn’t do anything like that,” he says. “We just put bison here. This is resilience that is inherent in the system. It just needed a little bit of a break from grazing to be able to do this all on its own.” What’s more, the creek is still improving, he says. “Every year the creek gets a little wider, a little more meandery, a little more like a pool and less like a trench.”
While the evidence for the benefits of bison is compelling, many cattle-owners think the story needs more nuance. Malou Anderson-Ramirez and her husband run cattle on a ranch bordering Yellowstone National Park, 300 miles (480km) to the south-west of American Prairie. When she talks about grazing and stream health, she inserts an important qualifier. “It’s not the cow, it’s the how,” she says. “If you graze cattle carefully, you can avoid the damage that occurs when they are left to their own devices,” says Anderson-Ramirez. She reinforces the places she wants cattle to cross a stream with rocks and fences. She pipes creek water into tanks hundreds of feet away to ensure animals aren’t wading into the stream to drink. She lets vegetation rest for several weeks between grazing rotations to give plants time to rebuild their roots. This type of regenerative grazing treats livestock as a tool that can improve the health of the land.
Shamon agrees that cattle can provide benefits in systems that evolved with large herbivores. In a study of grassland birds, she found that, outside of riparian areas, birds benefit almost as much from the presence of cattle as they do from bison. “If you manage the cattle in a proper way and you continue to rotate them, you could get an effect similar to bison,” Shamon says.
Kinka shares the view that grasslands need a big grazer, whether that be a cow or a bison. The key is to thwart cattle’s natural inclination to loiter in the water.
Martin Townsend of the Rancher’s Stewardship Alliance in Malta, Montana is helping ranchers implement these better grazing strategies. “Ranchers are very aware of what cows can do to riparian areas if left unattended,” he says. “They know it’s not in their interest.”
Conservationists often tout the benefits of bringing back top predators to restore balance to ecosystems. The importance of bringing back large, native grazers is lesser known but equally important. In Kansas, 30 years of bison grazing in tallgrass prairie has been shown to increase native plant species richness. In Europe, it is hoped the restoration of European bison in Kent in the UK will do something similar for ancient woodlands.
Across the world, native grazers are ready to slip back into ecosystems to resume their lost roles.

In places where native species reintroduction may be difficult, careful management of livestock can provide some of the same benefits. On landscapes as big as Montana’s prairie, it seems likely there is room for both. Besides, ranching still has an important place in the culture and economy of the regions like Montana.
But as climate change intensifies, it is worth considering which animals are best adapted to the emerging conditions. Plains bison, frugal around water and constantly on the move, are built for this land.
Bison are excellently doing their part to keep the prairie healthy.
By Alex Arlander | ENC News