Why life expectancy in the U.S. continues to decline in recent years

Life expectancy is the key metric for assessing population health.
According to CDC data, for the first time since World War II, life expectancy declined globally.
COVID cut average life spans short in many high-income countries, but the U.S. decline has been steeper and longer than most.
The graphic below is based on a data set that focuses mostly on Europe and the U.S., but similar trends emerged worldwide.
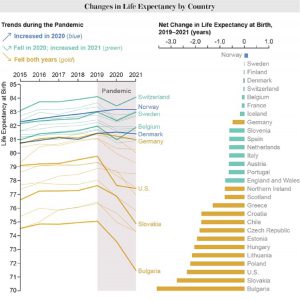
In the U.S., life expectancy fell from 78.8 years in 2019 to 77.3 years in 2020—the biggest peacetime decline on record.
In 2021 the average American could expect to live until age 76,4. That marks the lowest age since 1996 and the largest 2-year decline since 1923.
“Even small declines in life expectancy of a tenth or two-tenths of a year mean that on a population level, a lot more people are dying prematurely than they really should be,” said Robert Anderson, PhD, chief of mortality statistics at CDC’s the National Center for Health Statistics.

“This signals a huge impact on the population in terms of increased mortality,” he said.
COVID-19 played a major role, with excess death from the coronavirus contributing to half of the decline during the past 2 years.
Drug overdose deaths also reached a record high in 2021, rising to about 109,000 people.
The Faces of Fentanyl gallery of photos of fentanyl victims are seen at the DEA Headquarters in Arlington, Virginia, Thursday, December 8, 2022.

Unintentional injuries, with about half due to drug overdose, were a leading cause of the decline in life expectancy, along with deaths from heart disease, chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and suicide.
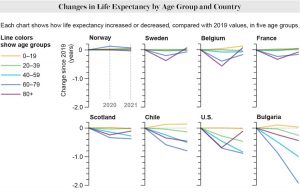
Life expectancy has fallen particularly sharply among Americans ages 40 to 59, a trend that reflects the opioid and homicide crises as well as COVID.
This human tragedy is compounded by an ominous economic dimension. Shorter life spans may presage slower growth in industries such as health care and financial services that cater to older people.
Falling life expectancy can also result in a smaller labor force, which in turn could have dire consequences; tax revenue could dry up, for example, and inflation could worsen if workers are scarce.
By Gilbert Castro | ENC News